CSAPP Bomb Lab - 2
Published:
Phase 4
Dump of assembler code for function phase_4:
0x000000000040100c <+0>: sub $0x18,%rsp
0x0000000000401010 <+4>: lea 0xc(%rsp),%rcx
0x0000000000401015 <+9>: lea 0x8(%rsp),%rdx
0x000000000040101a <+14>: mov $0x4025cf,%esi
0x000000000040101f <+19>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000401024 <+24>: callq 0x400bf0 <__isoc99_sscanf@plt>
0x0000000000401029 <+29>: cmp $0x2,%eax
0x000000000040102c <+32>: jne 0x401035 <phase_4+41>
0x000000000040102e <+34>: cmpl $0xe,0x8(%rsp)
0x0000000000401033 <+39>: jbe 0x40103a <phase_4+46>
0x0000000000401035 <+41>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x000000000040103a <+46>: mov $0xe,%edx
0x000000000040103f <+51>: mov $0x0,%esi
0x0000000000401044 <+56>: mov 0x8(%rsp),%edi
0x0000000000401048 <+60>: callq 0x400fce <func4>
0x000000000040104d <+65>: test %eax,%eax
0x000000000040104f <+67>: jne 0x401058 <phase_4+76>
0x0000000000401051 <+69>: cmpl $0x0,0xc(%rsp)
0x0000000000401056 <+74>: je 0x40105d <phase_4+81>
0x0000000000401058 <+76>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x000000000040105d <+81>: add $0x18,%rsp
0x0000000000401061 <+85>: retq
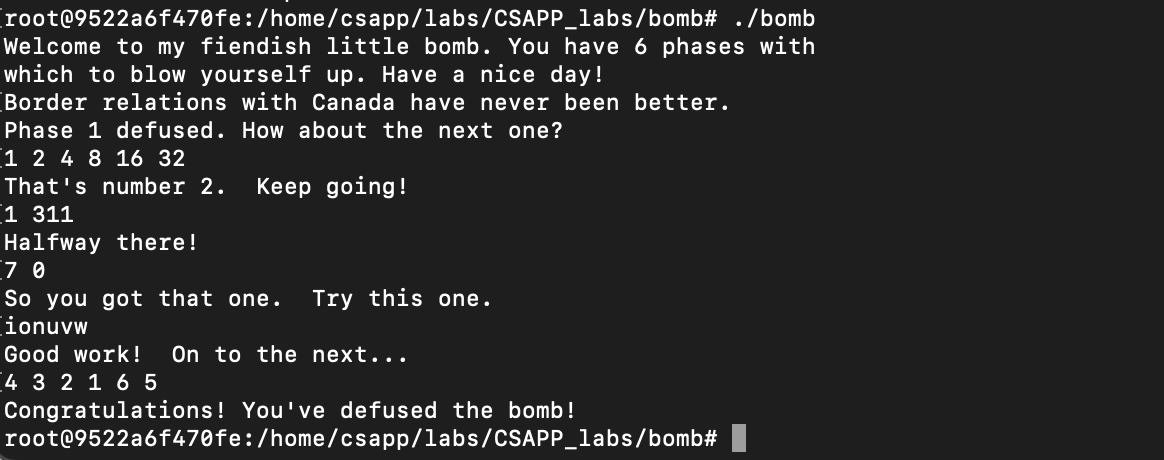
The codes before line +41 are not interesting, which indicates the first input must be below or eqaul to 0xe. Then, prepare three arguments for func4 procedure. The first argument is the first input. The second argument is 0, and the third is 0xe. The procedure func4 must return 0 otherwise the bomb explodes.
After returning from the procedure, it checks whether the second input is 0. So, the answer is 7 0.
func4
Dump of assembler code for function func4:
0x0000000000400fce <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x0000000000400fd2 <+4>: mov %edx,%eax
0x0000000000400fd4 <+6>: sub %esi,%eax
0x0000000000400fd6 <+8>: mov %eax,%ecx
0x0000000000400fd8 <+10>: shr $0x1f,%ecx
0x0000000000400fdb <+13>: add %ecx,%eax
0x0000000000400fdd <+15>: sar %eax
0x0000000000400fdf <+17>: lea (%rax,%rsi,1),%ecx
0x0000000000400fe2 <+20>: cmp %edi,%ecx
0x0000000000400fe4 <+22>: jle 0x400ff2 <func4+36>
0x0000000000400fe6 <+24>: lea -0x1(%rcx),%edx
0x0000000000400fe9 <+27>: callq 0x400fce <func4>
0x0000000000400fee <+32>: add %eax,%eax
0x0000000000400ff0 <+34>: jmp 0x401007 <func4+57>
0x0000000000400ff2 <+36>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000400ff7 <+41>: cmp %edi,%ecx
0x0000000000400ff9 <+43>: jge 0x401007 <func4+57>
0x0000000000400ffb <+45>: lea 0x1(%rcx),%esi
0x0000000000400ffe <+48>: callq 0x400fce <func4>
0x0000000000401003 <+53>: lea 0x1(%rax,%rax,1),%eax
0x0000000000401007 <+57>: add $0x8,%rsp
0x000000000040100b <+61>: retq
This is a recursive function and we want it to return 0. After the simulation, we find that it is close to binary searching process, which searches the first argument between the range of the second and third arguments. If it returns 0, the first argument can be the middle of the second and the third, which is \(\frac{0 + e}{2} = 7\).
Phase 5
Dump of assembler code for function phase_5:
0x0000000000401062 <+0>: push %rbx
0x0000000000401063 <+1>: sub $0x20,%rsp
0x0000000000401067 <+5>: mov %rdi,%rbx
0x000000000040106a <+8>: mov %fs:0x28,%rax
0x0000000000401073 <+17>: mov %rax,0x18(%rsp)
0x0000000000401078 <+22>: xor %eax,%eax
0x000000000040107a <+24>: callq 0x40131b <string_length>
0x000000000040107f <+29>: cmp $0x6,%eax
0x0000000000401082 <+32>: je 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112>
0x0000000000401084 <+34>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401089 <+39>: jmp 0x4010d2 <phase_5+112>
0x000000000040108b <+41>: movzbl (%rbx,%rax,1),%ecx
0x000000000040108f <+45>: mov %cl,(%rsp)
0x0000000000401092 <+48>: mov (%rsp),%rdx
0x0000000000401096 <+52>: and $0xf,%edx
0x0000000000401099 <+55>: movzbl 0x4024b0(%rdx),%edx
0x00000000004010a0 <+62>: mov %dl,0x10(%rsp,%rax,1)
0x00000000004010a4 <+66>: add $0x1,%rax
0x00000000004010a8 <+70>: cmp $0x6,%rax
0x00000000004010ac <+74>: jne 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010ae <+76>: movb $0x0,0x16(%rsp)
0x00000000004010b3 <+81>: mov $0x40245e,%esi
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
0x00000000004010b8 <+86>: lea 0x10(%rsp),%rdi
0x00000000004010bd <+91>: callq 0x401338 <strings_not_equal>
0x00000000004010c2 <+96>: test %eax,%eax
0x00000000004010c4 <+98>: je 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010c6 <+100>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004010cb <+105>: nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
0x00000000004010d0 <+110>: jmp 0x4010d9 <phase_5+119>
0x00000000004010d2 <+112>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x00000000004010d7 <+117>: jmp 0x40108b <phase_5+41>
0x00000000004010d9 <+119>: mov 0x18(%rsp),%rax
0x00000000004010de <+124>: xor %fs:0x28,%rax
0x00000000004010e7 <+133>: je 0x4010ee <phase_5+140>
0x00000000004010e9 <+135>: callq 0x400b30 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x00000000004010ee <+140>: add $0x20,%rsp
0x00000000004010f2 <+144>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004010f3 <+145>: retq
When encountering line +8, I have no idea what is
mov %fs:0x28,%rax. I have to check all I have learnt. I find this may help. Anyway, it seems to not relate to the bomb. So I will continue.
In the following few lines, it ensures that the length of the input string is 6. The core part begins from line +41, which transforms the input string character by character. The conversion is line +52, which only stores the lower 1 byte of the character as the offset. In line +55, the offset plus the base address 0x4024b0 is the target characters. The base address have the string “maduiersnfotvbyl”, which is the alphabet of the target string. The output string is line +81, “fliyer”. So, to construct this output string using the alphabet, the offset should be 9, f, e, 5, 6, 7. So, the characters of the input string must have the lower bytes in the offset series. After quering the ASCII table, one of the answer is ionuvw.
Phase 6
Dump of assembler code for function phase_6:
0x00000000004010f4 <+0>: push %r14
0x00000000004010f6 <+2>: push %r13
0x00000000004010f8 <+4>: push %r12
0x00000000004010fa <+6>: push %rbp
0x00000000004010fb <+7>: push %rbx
0x00000000004010fc <+8>: sub $0x50,%rsp
0x0000000000401100 <+12>: mov %rsp,%r13
0x0000000000401103 <+15>: mov %rsp,%rsi
0x0000000000401106 <+18>: callq 0x40145c <read_six_numbers>
0x000000000040110b <+23>: mov %rsp,%r14
0x000000000040110e <+26>: mov $0x0,%r12d
0x0000000000401114 <+32>: mov %r13,%rbp
0x0000000000401117 <+35>: mov 0x0(%r13),%eax
0x000000000040111b <+39>: sub $0x1,%eax
0x000000000040111e <+42>: cmp $0x5,%eax
0x0000000000401121 <+45>: jbe 0x401128 <phase_6+52>
0x0000000000401123 <+47>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401128 <+52>: add $0x1,%r12d
0x000000000040112c <+56>: cmp $0x6,%r12d
0x0000000000401130 <+60>: je 0x401153 <phase_6+95>
0x0000000000401132 <+62>: mov %r12d,%ebx
0x0000000000401135 <+65>: movslq %ebx,%rax
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
0x0000000000401138 <+68>: mov (%rsp,%rax,4),%eax
0x000000000040113b <+71>: cmp %eax,0x0(%rbp)
0x000000000040113e <+74>: jne 0x401145 <phase_6+81>
0x0000000000401140 <+76>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000401145 <+81>: add $0x1,%ebx
0x0000000000401148 <+84>: cmp $0x5,%ebx
0x000000000040114b <+87>: jle 0x401135 <phase_6+65>
0x000000000040114d <+89>: add $0x4,%r13
0x0000000000401151 <+93>: jmp 0x401114 <phase_6+32>
0x0000000000401153 <+95>: lea 0x18(%rsp),%rsi
0x0000000000401158 <+100>: mov %r14,%rax
0x000000000040115b <+103>: mov $0x7,%ecx
0x0000000000401160 <+108>: mov %ecx,%edx
0x0000000000401162 <+110>: sub (%rax),%edx
0x0000000000401164 <+112>: mov %edx,(%rax)
0x0000000000401166 <+114>: add $0x4,%rax
0x000000000040116a <+118>: cmp %rsi,%rax
0x000000000040116d <+121>: jne 0x401160 <phase_6+108>
0x000000000040116f <+123>: mov $0x0,%esi
0x0000000000401174 <+128>: jmp 0x401197 <phase_6+163>
0x0000000000401176 <+130>: mov 0x8(%rdx),%rdx
0x000000000040117a <+134>: add $0x1,%eax
0x000000000040117d <+137>: cmp %ecx,%eax
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
0x000000000040117f <+139>: jne 0x401176 <phase_6+130>
0x0000000000401181 <+141>: jmp 0x401188 <phase_6+148>
0x0000000000401183 <+143>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x0000000000401188 <+148>: mov %rdx,0x20(%rsp,%rsi,2)
0x000000000040118d <+153>: add $0x4,%rsi
0x0000000000401191 <+157>: cmp $0x18,%rsi
0x0000000000401195 <+161>: je 0x4011ab <phase_6+183>
0x0000000000401197 <+163>: mov (%rsp,%rsi,1),%ecx
0x000000000040119a <+166>: cmp $0x1,%ecx
0x000000000040119d <+169>: jle 0x401183 <phase_6+143>
0x000000000040119f <+171>: mov $0x1,%eax
0x00000000004011a4 <+176>: mov $0x6032d0,%edx
0x00000000004011a9 <+181>: jmp 0x401176 <phase_6+130>
0x00000000004011ab <+183>: mov 0x20(%rsp),%rbx
0x00000000004011b0 <+188>: lea 0x28(%rsp),%rax
0x00000000004011b5 <+193>: lea 0x50(%rsp),%rsi
0x00000000004011ba <+198>: mov %rbx,%rcx
0x00000000004011bd <+201>: mov (%rax),%rdx
0x00000000004011c0 <+204>: mov %rdx,0x8(%rcx)
0x00000000004011c4 <+208>: add $0x8,%rax
0x00000000004011c8 <+212>: cmp %rsi,%rax
0x00000000004011cb <+215>: je 0x4011d2 <phase_6+222>
0x00000000004011cd <+217>: mov %rdx,%rcx
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
0x00000000004011d0 <+220>: jmp 0x4011bd <phase_6+201>
0x00000000004011d2 <+222>: movq $0x0,0x8(%rdx)
0x00000000004011da <+230>: mov $0x5,%ebp
0x00000000004011df <+235>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rax
0x00000000004011e3 <+239>: mov (%rax),%eax
0x00000000004011e5 <+241>: cmp %eax,(%rbx)
0x00000000004011e7 <+243>: jge 0x4011ee <phase_6+250>
0x00000000004011e9 <+245>: callq 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x00000000004011ee <+250>: mov 0x8(%rbx),%rbx
0x00000000004011f2 <+254>: sub $0x1,%ebp
0x00000000004011f5 <+257>: jne 0x4011df <phase_6+235>
0x00000000004011f7 <+259>: add $0x50,%rsp
0x00000000004011fb <+263>: pop %rbx
0x00000000004011fc <+264>: pop %rbp
0x00000000004011fd <+265>: pop %r12
0x00000000004011ff <+267>: pop %r13
0x0000000000401201 <+269>: pop %r14
0x0000000000401203 <+271>: retq
The codes before line +18 aim to store the six integer from the beginning of the stack pointer. The codes from line +32 to +93 aim to check all the numbers are different, and they must be below or equal to 6. The codes from line +95 to +121 aim to replace each input number with the 7-x where x is each number.
line +123 - +181: for every 7-x, if it is equal to 1 (i.e. x = 6), put 0x6032d0 into 0x20 + %rsp + 8 * index of this element. So, every element now sits on 8 bytes starting from addresss 0x20 + %rsp. If it is larger than 1, calculate the difference of 7-x and 1 as y. There is a linked list in the stack, which starting from the address 0x6032d0, since the following memory dump:
(gdb) x/2wx 0x6032d8
0x6032d8 <node1+8>: 0x006032e0 0x00000000
(gdb) x/2wx 0x6032e8
0x6032e8 <node2+8>: 0x006032f0 0x00000000
(gdb) x/2wx 0x6032f8
0x6032f8 <node3+8>: 0x00603300 0x00000000
(gdb) x/2wx 0x603308
0x603308 <node4+8>: 0x00603310 0x00000000
(gdb) x/2wx 0x603318
0x603318 <node5+8>: 0x00603320 0x00000000
(gdb) x/2wx 0x603328
0x603328 <node6+8>: 0x00000000 0x00000000
The code will store the pointer to the linked list node at the 0x20 + %rsp + 8 * index of this element. The node index is y for every element.
line +183 - +222: starting from 0x20 + %rsp, for every pointer, set the ith pointer’s next (in the memory) as the (i+1)th pointer. And set the 6th pointer’s next as 0x0.
line +230 - end: the value stored at the first pointer to the sixth pointer should be descending. So, we must check the values stored at each pointer.
(gdb) x/wx 0x6032d0
0x6032d0 <node1>: 0x0000014c
(gdb) x/wx 0x6032e0
0x6032e0 <node2>: 0x000000a8
(gdb) x/wx 0x6032f0
0x6032f0 <node3>: 0x0000039c
(gdb) x/wx 0x603300
0x603300 <node4>: 0x000002b3
(gdb) x/wx 0x603310
0x603310 <node5>: 0x000001dd
(gdb) x/wx 0x603320
0x603320 <node6>: 0x000001bb
node3 > node4 > node5 > node6 > node1 > node2
So, the first element has difference 2, the node4 pointer has difference 3, …
So, \(7 - x - 1 = 2 => x = 4\), \(7 - x - 1 = 3 => x = 3\), … The answer is 4 3 2 1 6 5.
Finally
This lab is so painful… Tortures my mind and eyes to decode the assembly language.
But congratulations to myself!